Difference between revisions of "Contrib:KeesWouters/plasticity/solidbeam"
Keeswouters (Talk | contribs) m (→''The results of the linear calculation'') |
Keeswouters (Talk | contribs) (→''The results of the linear calculation'') |
||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
| | | | ||
LinRes=CALC_ELEM(reuse = LinRes, | LinRes=CALC_ELEM(reuse = LinRes, | ||
| − | + | INFO=2, | |
| − | + | CRITERE='RELATIF', | |
| − | + | TYPE_OPTION='TOUTES', | |
| − | + | OPTION=('SIGM_ELNO_DEPL','EQUI_ELNO_SIGM','SIEF_ELNO_ELGA', | |
| − | + | 'EPSI_ELNO_DEPL','EQUI_ELNO_EPSI',), | |
| − | + | SOLVEUR=_F(RENUM='METIS',STOP_SINGULIER='OUI', | |
| − | + | METHODE='MULT_FRONT',NPREC=8), | |
| − | + | PRECISION=9.9999999999999995E-07, | |
| − | + | RESULTAT=LinRes,); | |
| | | | ||
calculate element results | calculate element results | ||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
EPSI_ELNO_DEPL --> local strains EPSab | EPSI_ELNO_DEPL --> local strains EPSab | ||
EQUI_ELNO_EPSI --> equivalent strains | EQUI_ELNO_EPSI --> equivalent strains | ||
| + | |||
| + | OPTION defaults to: OPTION='SIEF_ELNO_ELGA' | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 2 May 2010
Contents
Solid beam under plastic deformation
[... not ready yet ...]
This contribution has been created because of some incompatibilities between version CA10.X.Y and earlier versions. For detailed description of the calculation sequence look here.
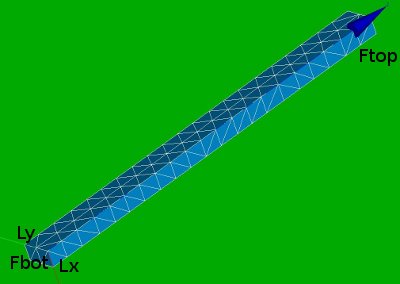
Geometry and mesh of the solid beam
Using a straight solid beam is easy for analysis of the stresses and strains.
Fbot and Ftop are the bottom and top surfaces.
Lx and Ly are the edges along the x and y axes.
Non linear material behaviour
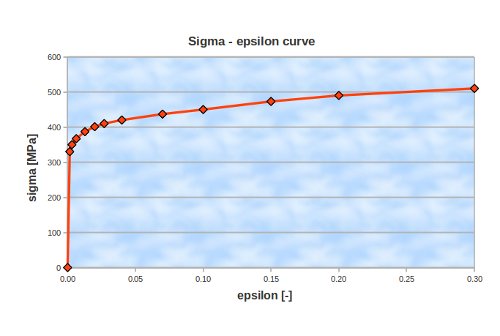
The non linear material behaviour is defined by the sigma epsilon curve. The CA commands for this relation are given by DEFI_FONCTION and DEFI_MATERIAU. The curve that has been used in this calculation is depicted below.
Sigma_eps = DEFI_FONCTION(NOM_PARA='EPSI',
VALE=(0.0016, 330,
0.0032, 350,
0.0064, 367,
0.0128, 387,
0.0200, 401,
0.0270, 410,
0.0400, 420,
0.0700, 437,
0.1000, 450,
0.1500, 473,
0.2000, 490,
0.3000, 510,),
INTERPOL='LIN',PROL_DROITE='LINEAIRE',PROL_GAUCHE='EXCLU',);
#define plastic behaviour of steel by Sigma_eps
steel=DEFI_MATERIAU(ELAS=_F(E=2.1e5,NU=0.27,),
TRACTION=_F(SIGM=Sigma_eps,),);
Note that the origin need not to be specified for the sigma epsilon in the DEFI_FONCTION.
The boundary conditions and the loads
For the boundary conditions we choose to fix:
- the bottom plane in axial (z) direction,
- the edge along the x axis in y direction and
- the edge along the y axis in x direction
LoadFix=AFFE_CHAR_MECA(MODELE=pmode,
FACE_IMPO=(_F(GROUP_MA='Fbot',DZ=0.0,),),
DDL_IMPO=(_F(GROUP_MA='Lx',DY=0.0),
_F(GROUP_MA='Ly',DX=0.0),),);
For the load we apply an axial force on the top plane. The force is gradually increased to its maximum value, kept constant and reduced to zero again. This is performed by the multiplification function ramp in the load command.
# LoadPres will vary in the nonlinear calculation determined by the 'time' and 'ramp' function
# number of 'time' steps tsteps
# ramp increases during:
# 1.2 s: from 0.0 to 1.0,
# 0.1 s: constant at 1.0
# 0.7 s: from 1.0 down to 0.3
dt = 0.10
t0 = 0.00
t1 = 1.20
t2 = t1+dt
t3 = 2.00
tsteps = int(t3*10)
disp = 0.0750
LoadPres=AFFE_CHAR_MECA(MODELE=pmode,
FACE_IMPO=(_F(GROUP_MA='Ftop',DZ=disp,),),);
ramp=DEFI_FONCTION(NOM_PARA='INST',
VALE=(t0,0.00,
t1,1.00,
t2,1.00,
t3,0.30,),
INFO=2,TITRE='ramp',);
time=DEFI_LIST_REEL(DEBUT=0.0,
INTERVALLE=_F(JUSQU_A=t3,NOMBRE=tsteps,),
INFO=2,TITRE='time',);
deflist = DEFI_LIST_INST(DEFI_LIST=_F(METHODE ='AUTO',
LIST_INST = time,
PAS_MINI = 0.0005),)
Presul=STAT_NON_LINE(MODELE=pmode,
CHAM_MATER=matprops,
EXCIT=(_F(CHARGE=LoadFix,),
_F(CHARGE=LoadPres,FONC_MULT=ramp,),),
COMP_INCR=_F(RELATION='VMIS_ISOT_TRAC',
DEFORMATION='SIMO_MIEHE',
TOUT='OUI',),
INCREMENT=_F(LIST_INST= deflist,), #time,
NEWTON=_F(REAC_INCR=1,
MATRICE='TANGENTE',
REAC_ITER=1,),
CONVERGENCE=_F(ITER_GLOB_MAXI=20,),
ARCHIVAGE=_F(PAS_ARCH=1,),);
For comparison the linear calculation is applied as well:
LinRes=MECA_STATIQUE(MODELE=pmode,
CHAM_MATER=matprops,
#CARA_ELEM=shellch,
EXCIT=(_F(CHARGE=LoadFix,),
_F(CHARGE=LoadPres,),),);
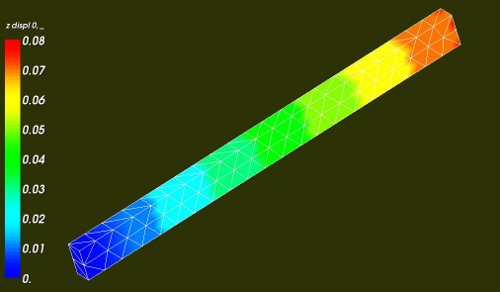
The results
The results of the linear calculation
SIEF_ELNO_ELGA numero d'ordre 1 pour le calcul de l'option SIEF_NOEU_ELGA
| commands to determine stresses and strains | |
|---|---|
POURSUITE(); |
***** |
LinRes=CALC_ELEM(reuse = LinRes,
INFO=2,
CRITERE='RELATIF',
TYPE_OPTION='TOUTES',
OPTION=('SIGM_ELNO_DEPL','EQUI_ELNO_SIGM','SIEF_ELNO_ELGA',
'EPSI_ELNO_DEPL','EQUI_ELNO_EPSI',),
SOLVEUR=_F(RENUM='METIS',STOP_SINGULIER='OUI',
METHODE='MULT_FRONT',NPREC=8),
PRECISION=9.9999999999999995E-07,
RESULTAT=LinRes,);
|
calculate element results SIGM_ELNO_DEPL --> local stresses SIab EQUI_ELNO_SIGM --> equivalent stresses VMIS,TRESCA,.. SIEF_ELNO_ELGA --> equivalent stresses at gauss points EPSI_ELNO_DEPL --> local strains EPSab EQUI_ELNO_EPSI --> equivalent strains OPTION defaults to: OPTION='SIEF_ELNO_ELGA' |
LinRes=CALC_NO(reuse =LinRes,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
OPTION= ('SIEF_NOEU_ELGA','SIGM_NOEU_DEPL','EQUI_NOEU_SIGM',
'FORC_NODA','REAC_NODA',),);
|
calculate nodal equivalents and reaction forces SIEF_ELNO_ELGA --> SIEF_NOEU_ELGA --> equivalent stresses at gauss points SIGM_ELNO_DEPL --> SIGM_NOEU_DEPL --> local stresses SIab EQUI_ELNO_SIGM --> EQUI_NOEU_SIGM --> equivalent stresses VMIS, TRESCA, ... FORC_NODA --> nodal forces REAC_NODA --> reaction forces |
IMPR_RESU(FORMAT='MED',
UNITE=80,
RESU=(_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='DEPL',
NOM_CMP=('DX','DY','DZ',),),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='SIEF_NOEU_ELGA',),
#NOM_CMP=('SIXX','SIYY','SIZZ',),),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='SIGM_NOEU_DEPL',),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EQUI_ELNO_SIGM',),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EQUI_NOEU_SIGM',),),);
|
write fields to med file |
IMPR_RESU(FORMAT='MED',
UNITE=80,
RESU=(_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='DEPL',
NOM_CMP=('DX','DY','DZ',),),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='SIEF_NOEU_ELGA',),
#NOM_CMP=('SIXX','SIYY','SIZZ',),),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='SIGM_NOEU_DEPL',),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EQUI_ELNO_SIGM',),
_F(MAILLAGE=pmesh,
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EQUI_NOEU_SIGM',),),);
|
write fields to med file |
IMPR_RESU(FORMAT='MED',
UNITE=80,
RESU=(_F(RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EPSI_ELNO_DEPL',),
_F(RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='EQUI_ELNO_EPSI',),),);
|
write strains to med file |
pmesh=DEFI_GROUP(reuse =pmesh,
MAILLAGE=pmesh,
CREA_GROUP_NO=_F(NOM='Nreac',GROUP_MA='Fbot',),);
pmesh=DEFI_GROUP(reuse =pmesh,
MAILLAGE=pmesh,
CREA_GROUP_NO=_F(NOM='Nforce',GROUP_MA='Ftop',),);
|
define groups of nodes from geometrical entities 'Ftop' and 'Fbot' |
TB_nodf=POST_RELEVE_T(ACTION=(_F(OPERATION='EXTRACTION',
INTITULE='displacements',
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='DEPL',
TOUT_ORDRE='OUI',
GROUP_NO='Nforce',
RESULTANTE=('DX','DY','DZ',),
MOYE_NOEUD='NON',),
_F(OPERATION='EXTRACTION',
INTITULE='ReactionForces',
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='REAC_NODA',
TOUT_ORDRE='OUI',
GROUP_NO='Nreac',
RESULTANTE=('DX','DY','DZ',),
MOYE_NOEUD='NON',),
_F(OPERATION='EXTRACTION',
INTITULE='NodalForces',
RESULTAT=LinRes,
NOM_CHAM='FORC_NODA',
PRECISION=0.000001,
GROUP_NO='Nreac',
RESULTANTE=('DX','DY','DZ',),),),
TITRE='[Reaction] Nodal Forces',);
|
define fields to write to the table TB_nodf |
IMPR_TABLE(TABLE=TB_nodf,
FORMAT='TABLEAU',
UNITE=26,
SEPARATEUR=' * ',
TITRE='displacements at nodes on group Nforce',);
|
write table TB_nodf to file |
-
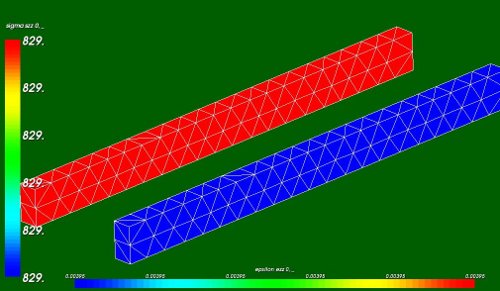
- Elastic axial stresses sigma_zz (green beam, value 829 [MPa]) and strains eps_zz (blue beam, 3.95 [mm/m])
Theoretical verification:
- length of the beam: 19 mm
- cross section: 0.8*1.5 = 1.2 mm2
- Young's module: E = 2.1e5 MPa
- In the linear case, this yields a stress sigma and strain epsilon:
- epsilon e_zz = dz/Lz = 0.075/19 = 0.00395 ~ 0.004 [-]
- sigma = e_zz*E = 829 MPa
- On the top 15 nodes the displacements and reaction forces are:
- dz = 1.12500E+00 [mm] --> 0.075 mm at each node (that is correct)
- Rz = -9.94737E+02 [N] --> pressure is Rz/A = -9.94737E+02/1.2 = 829 MPa (that is correct as well).