Contrib:KeesWouters/prestressmodal
Contents
Modal analysis of a cylinder under prestress
To start with, this contribution mainly focuses on the use of Salome and Code Aster, not on the results and the mechanical justifications of the code that has been used. So no guarantee that the results will be correct up to the fifth decimal place, which they are not. I do hope though that this information is useful. For me it has been, because I had to think about some commands and look through the documentation and learn from that. In case of mistakes, errors and the like, please notify me, or better, you are invited to correct them yourself. Enjoy.
As usual, the files that define the geometry, mesh and command files can be found at the end of this contribution.
Defining the properties of the cylinder
Geometry of the cylinder
The construction is by extrusion cq piping from a circle with diameter 4 mm. The extrusion is defined along a path along the z axis, defined by six points *). The main commands of the python script are:
- define points: pz1 = geompy.MakeVertex(0.00, 0, 1)
- define circle: Circle = geompy.MakeCircle(centre, vector, radius)
- define path: Curve = geompy.MakePolyline([null, pz1, pz2, pz3, pz4, pz5 ])
- define cylinder: Pipe = geompy.MakePipe(Circle, Curve)
*) I used six points to do some experiments with the Pipe command. Of course, here is not necessary to use six points.
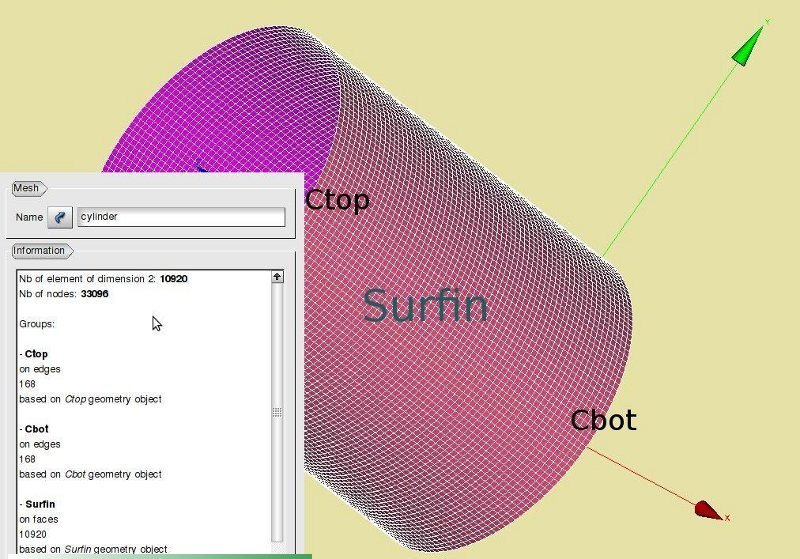
For applying boundary conditions and loads and use the shell elements later in the command file of Code Aster, we define the top and bottom circumference of the cylinder and the cylinder area:
- Surfin = geompy.CreateGroup(Pipe, geompy.ShapeType["FACE"])
- geompy.UnionIDs(Surfin, [25, 20, 15, 10, 3])
- Pipe = geompy.GetMainShape(Surfin)
- Ctop = geompy.CreateGroup(Pipe, geompy.ShapeType["EDGE"])
- geompy.UnionIDs(Ctop, [29])
- Pipe = geompy.GetMainShape(Ctop)
- Cbot = geompy.CreateGroup(Pipe, geompy.ShapeType["EDGE"])
- geompy.UnionIDs(Cbot, [8])
- Pipe = geompy.GetMainShape(Cbot)
The mesh of the cylinder
The mesh is define in a python script. It is generated by NetGen 1D_2D. By allowing quadrangles, a regular mesh with only this type of elements occur. Further options are: maxsize is 0.075, optimise, fineness is 3 and use second order, that is needed for coque_3d elements. Note the these quadratic quadrangles (quad8) need to be adapted to quad9 elements to be compatible with coque_elements in the command file.
The names of the axial end of the circumference and shell area of the cylinder are denoted by Cbot, Ctop and Surfin.
The load and boundary conditions of the cylinder
The load and boundary conditions are defined in the Code Aster command file. The boundary conditions are at Ctop:
- restrict displacements and rotations dx=dy=dz=drx=dry=drz=0
- DDL_IMPO=(_F(GROUP_MA=('Cbot'),DX=0.0,DY=0.0,DZ=0.0,DRX=0.0,...),...
- restrict displacements and rotations dx=dy=drx=dry=drz=0 except dz
- DDL_IMPO=(...._F(GROUP_MA=('Ctop'),DX=0.0,DY=0.0,DRX=0.0,...),...
The load on the construction is an axial line force
- Fclamp=AFFE_CHAR_MECA(...,FORCE_ARETE=_F(GROUP_MA='Ctop',FZ=+Fax/Lcyl,),);
Material properties of the beam
The beam consists of steel.
- steel=DEFI_MATERIAU(ELAS=_F(E=2.100e5,NU=0.28,RHO=0.007850),);