Difference between revisions of "Contrib:BondMatt/LaminarPipeFlow"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<br/><br/> '''Geometry''' | <br/><br/> '''Geometry''' | ||
<br/> The geometry is a box. The Cornell tutorial uses a 2-D box but Code Saturne can only work with 3-D geometry. The box represents a cross section of a pipe along its length cut in half to take advantage of the flow symmetry around the axis of the pipe. I created a box using the 'create a box' icon which brings up the same dialogue box if one goes to 'New Entity' and then 'Primitives' and then 'Box' in the task bar. | <br/> The geometry is a box. The Cornell tutorial uses a 2-D box but Code Saturne can only work with 3-D geometry. The box represents a cross section of a pipe along its length cut in half to take advantage of the flow symmetry around the axis of the pipe. I created a box using the 'create a box' icon which brings up the same dialogue box if one goes to 'New Entity' and then 'Primitives' and then 'Box' in the task bar. | ||
| − | [[Image:box.jpg]] | + | <br/>[[Image:box.jpg]] |
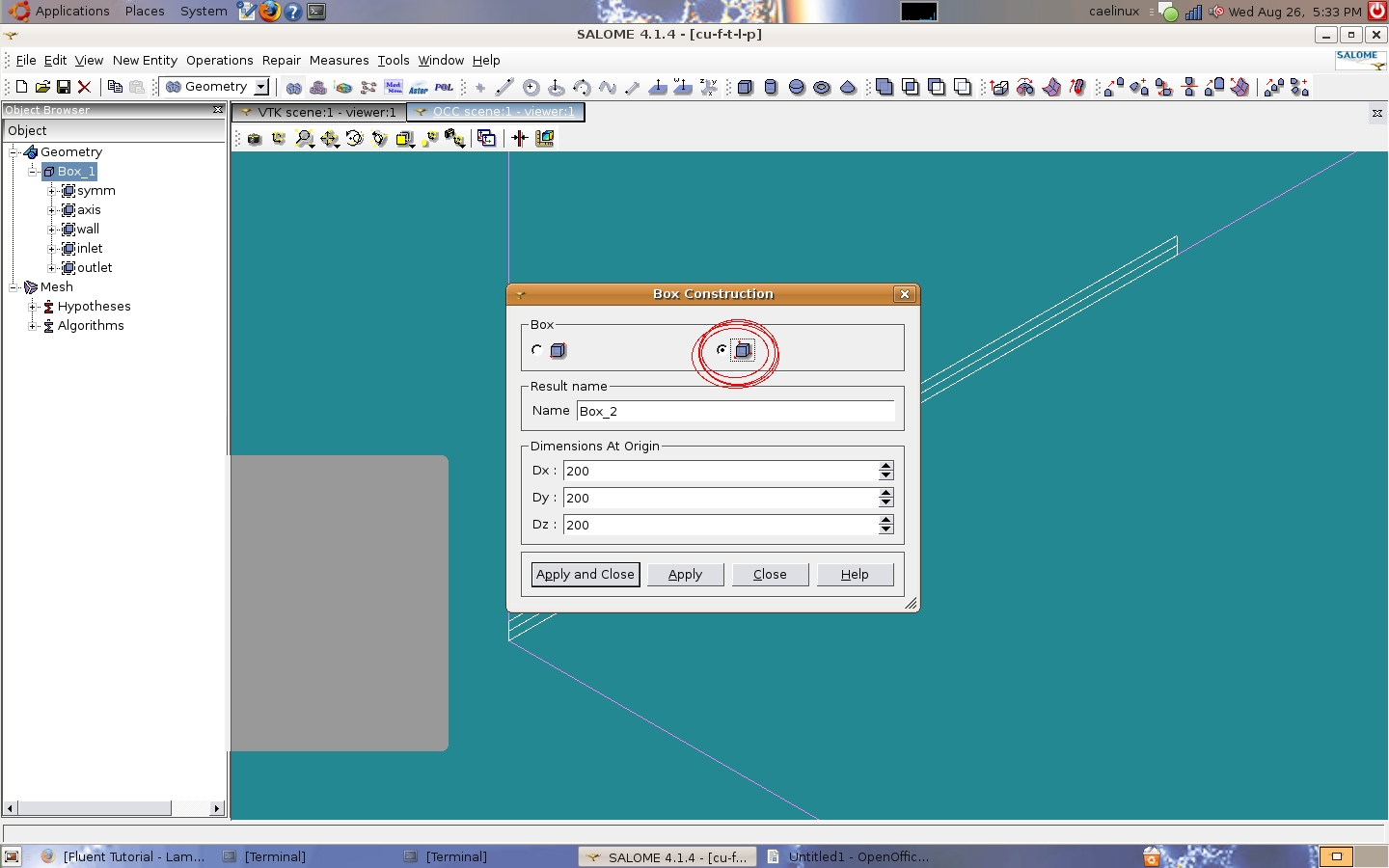
| − | Dx is the width of the box in the x-direction, starting at the origin. My dimensions: Dx=0.001, Dy=8, and Dz=0.1 Units are meters. The next step is to create the groups of faces for boundary conditions. As in the Cornell tutorial, half the pipe is studied to take advantage of symmetry. There are three symmetry B.C.s, one inlet B.C., one outlet B.C., and a wall B.C. | + | <br/>Dx is the width of the box in the x-direction, starting at the origin. My dimensions: Dx=0.001, Dy=8, and Dz=0.1 Units are meters. The next step is to create the groups of faces for boundary conditions. As in the Cornell tutorial, half the pipe is studied to take advantage of symmetry. There are three symmetry B.C.s, one inlet B.C., one outlet B.C., and a wall B.C. |
<br/>[[Image:box2.jpg]] | <br/>[[Image:box2.jpg]] | ||
<br/>Groups can be created by going to 'New Entity', 'Group', and then 'Create'. When creating a group the elements are selected by type (points, lines, planes, solids) and added with the 'add' button. Descriptive group names should be used to make applying B.C.s easier. Once all elements for a group are selected and the name is specified the 'Apply' button is clicked. | <br/>Groups can be created by going to 'New Entity', 'Group', and then 'Create'. When creating a group the elements are selected by type (points, lines, planes, solids) and added with the 'add' button. Descriptive group names should be used to make applying B.C.s easier. Once all elements for a group are selected and the name is specified the 'Apply' button is clicked. | ||
Revision as of 06:17, 5 September 2009
Software Versions:
Ubuntu 8.04 LTS
Salome V4.1.4
Code Saturne V1.4.a (GUI)
Fluent Tutorial
The Cornell University Fluent tutorial can be found here Cornell Tutorial
Geometry
The geometry is a box. The Cornell tutorial uses a 2-D box but Code Saturne can only work with 3-D geometry. The box represents a cross section of a pipe along its length cut in half to take advantage of the flow symmetry around the axis of the pipe. I created a box using the 'create a box' icon which brings up the same dialogue box if one goes to 'New Entity' and then 'Primitives' and then 'Box' in the task bar.
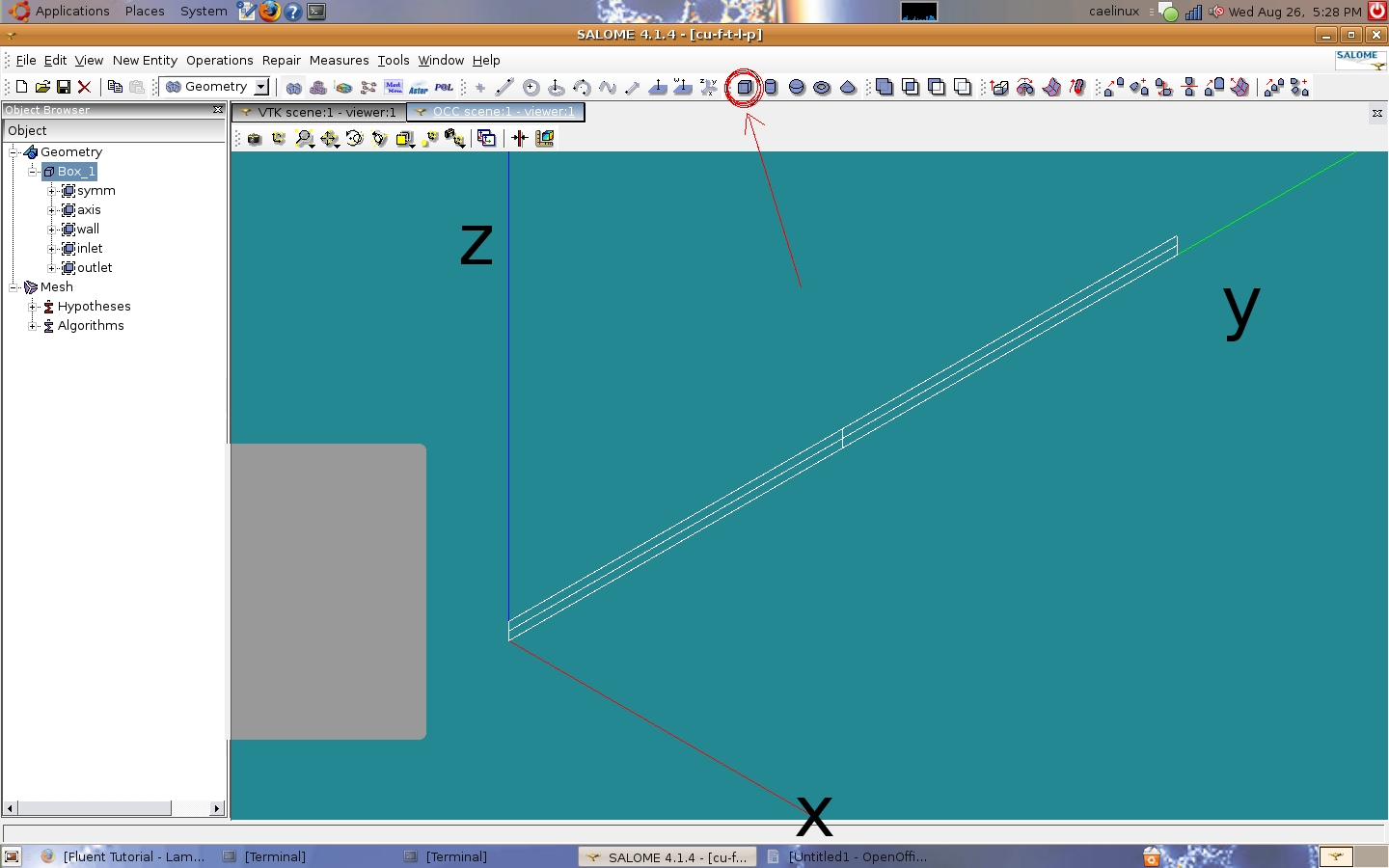
Dx is the width of the box in the x-direction, starting at the origin. My dimensions: Dx=0.001, Dy=8, and Dz=0.1 Units are meters. The next step is to create the groups of faces for boundary conditions. As in the Cornell tutorial, half the pipe is studied to take advantage of symmetry. There are three symmetry B.C.s, one inlet B.C., one outlet B.C., and a wall B.C.
Groups can be created by going to 'New Entity', 'Group', and then 'Create'. When creating a group the elements are selected by type (points, lines, planes, solids) and added with the 'add' button. Descriptive group names should be used to make applying B.C.s easier. Once all elements for a group are selected and the name is specified the 'Apply' button is clicked.