Difference between revisions of "Contrib:Johnnygeling/springplate"
Johnnygeling (Talk | contribs) (→''Result'') |
Johnnygeling (Talk | contribs) m (→Displacement field) |
||
| Line 203: | Line 203: | ||
==='''Coque_3D'''=== | ==='''Coque_3D'''=== | ||
====Displacement field==== | ====Displacement field==== | ||
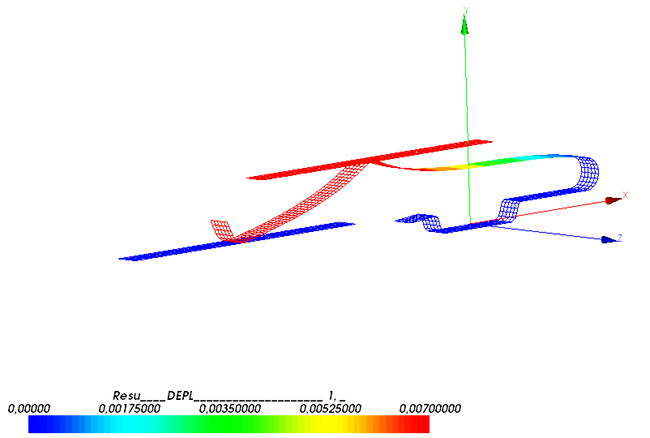
| − | The deformation after the last load step is shown | + | The deformation after the last load step with the 2 contact zones is shown below. |
[[Image:Final_displacement.png]] | [[Image:Final_displacement.png]] | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 9 May 2010
Contents
Sheetmetal spring with contact (shell elements with contact)
under construction (johnnygeling 10:09, 17 April 2010 (CEST))
Introduction
This contribution mainly focuses on the use of Salome, Code Aster and particular howto deal with shell elements and contact. So I do not focus on the results and the mechanical justifications of the code that has been used. So no guarantee that the results will be correct up to five decimal places, which they are probably not. I do hope though that this information is useful. For me it has been, because I had to think about some commands and look through the documentation and learn from that. In case of mistakes, errors or remarks, please notify me, or better, you are invited to correct or edit them yourself. Enjoy.
The geometry
The geometry and the mesh of the construction
The description of this problem is shown in the picture:
The mesh
The mesh is divided in three components:
- drive
- bladveer
- wall
The assemble mesh is shown:
The model
The .comm files:
coque_3d
There are three mesh-files to be read, for each component one.
Read mesh file of 'bladveer' component
bladveer=LIRE_MAILLAGE(UNITE=20,
FORMAT='MED',
VERI_MAIL=_F(VERIF='OUI',),);
Read mesh file of 'drive' component
drive=LIRE_MAILLAGE(UNITE=21,
FORMAT='MED',
VERI_MAIL=_F(),);
Read mesh file of 'wall' component
wall=LIRE_MAILLAGE(UNITE=22,
FORMAT='MED',
VERI_MAIL=_F(),);
Assemble 2 meshes into a temporary mesh:
temp_m=ASSE_MAILLAGE(MAILLAGE_1=bladveer,
MAILLAGE_2=drive,
OPERATION='SUPERPOSE',);
Assemble the temporary mesh with the last mesh:
mesh=ASSE_MAILLAGE(MAILLAGE_1=temp_m,
MAILLAGE_2=wall,
OPERATION='SUPERPOSE',);
Transform the quad mesh with 8 node into a quad mesh with 9 nodes:
meshQ=CREA_MAILLAGE(MAILLAGE=mesh,
MODI_MAILLE=_F(TOUT='OUI',
OPTION='QUAD8_9',),);
Orientation of the surfaces:
meshQ=MODI_MAILLAGE(reuse =meshQ,
MAILLAGE=meshQ,
ORIE_NORM_COQUE=_F(GROUP_MA=('f_wall','f_reac_c',),),);
Define material properties. (Be aware of the units of the mesh)
staal=DEFI_MATERIAU(ELAS=_F(E=2.1E11,
NU=0.3,),);
Apply material to domain:
Appl_mat=AFFE_MATERIAU(MAILLAGE=meshQ,
AFFE=_F(TOUT='OUI',
MATER=staal,),);
Create model:
model=AFFE_MODELE(MAILLAGE=meshQ,
VERIF=('MAILLE','NOEUD',),
AFFE=_F(TOUT='OUI',
PHENOMENE='MECANIQUE',
MODELISATION='COQUE_3D',),);
Boundary conditions of fixed elements:
randvw3=AFFE_CHAR_CINE(MODELE=model,
MECA_IMPO=(_F(GROUP_MA=('f_wall','f_fix_1',),
DX=0.0,
DY=0.0,
DZ=0.0,
DRX=0.0,
DRY=0.0,
DRZ=0.0,),
_F(GROUP_MA=('f_reac_c','f_bladv',),
DZ=0.0,),),);
Contact definitions:
cont1=AFFE_CHAR_MECA(MODELE=model,
CONTACT=(_F(METHODE='CONTRAINTE',
GROUP_MA_MAIT='f_drive',
GROUP_MA_ESCL='f_load_c',
APPARIEMENT='MAIT_ESCL',
LISSAGE='NON',
NORMALE='MAIT',
TYPE_APPA='PROCHE',
TOLE_APPA=0.01,
REAC_GEOM='AUTOMATIQUE',),
_F(METHODE='CONTRAINTE',
GROUP_MA_MAIT='f_wall',
GROUP_MA_ESCL='f_reac_c',
APPARIEMENT='MAIT_ESCL',
LISSAGE='NON',
NORMALE='MAIT',
TYPE_APPA='PROCHE',
TOLE_APPA=0.01,
REAC_GEOM='AUTOMATIQUE',),),);
Load condition. In this case f_drive is moved 7mm downwards
load=AFFE_CHAR_MECA(MODELE=model,
DDL_IMPO=_F(GROUP_MA='f_drive',
DX=0.0,
DY=-0.007,
DZ=0.0,),);
Thickness and orientation of shell elements:
shell=AFFE_CARA_ELEM(MODELE=model,
COQUE=_F(GROUP_MA=('f_wall','f_bladv','f_drive',),
EPAIS=0.0003,),);
Direction of load curve:
LinRamp=DEFI_FONCTION(NOM_PARA='INST',VALE=(0.0,0.0,
1.0,1.0,
),PROL_DROITE='LINEAIRE',PROL_GAUCHE='LINEAIRE',);
Loadstep. Load of 7mm is divided into small steps. In this case each load step is 7mm * 0.05/1 = 0,35mm
List=DEFI_LIST_REEL(DEBUT=0.,
INTERVALLE=_F(JUSQU_A=1.0,
PAS=0.05,),);
The non-linear calculation:
Resu=STAT_NON_LINE(MODELE=model,
CHAM_MATER=Appl_mat,
CARA_ELEM=shell,
EXCIT=(_F(CHARGE=randvw3,),
_F(CHARGE=load,
FONC_MULT=LinRamp,),
_F(CHARGE=cont1,),),
COMP_INCR=_F(RELATION='ELAS',
DEFORMATION='REAC_GEOM',),
INCREMENT=_F(LIST_INST=List,
PRECISION=1.E-6,),
CONVERGENCE=_F(RESI_GLOB_MAXI=1.E-4,
RESI_GLOB_RELA=1.E-4,
ITER_GLOB_MAXI=30,
TYPE='PIC',),
SOLVEUR=_F(METHODE='MULT_FRONT',
SYME='OUI',),
METHODE='NEWTON',
NEWTON=_F(REAC_INCR=1,
PREDICTION='TANGENTE',
MATRICE='TANGENTE',
REAC_ITER=1,
REAC_ITER_ELAS=1,),);
Primary results. All available results will be written in de result file. The result file is in MED-format. Available fields are:
- DEPL : Displacements
- VALE_CONT
- SIEF_ELGA : Stresses in element gauss points (Correct?)
- VARI_ELGA : Internal variables
Other results will be extracted with another .comm file:
IMPR_RESU(FORMAT='MED',
UNITE=80,
RESU=_F(MAILLAGE=meshQ,
RESULTAT=Resu,
INFO_MAILLAGE='OUI',
TOUT_CHAM='OUI',),);
FIN();
dkt
contact
Result
Coque_3D
Displacement field
The deformation after the last load step with the 2 contact zones is shown below.